|
|
@@ -22,19 +22,19 @@
|
|
|
Open the `bsp`'s `env` interface, go to **->RT-Thread online packages->IoT**, and find **[*] P-Net stack for Profinet device implementation --->** to enable it. Also, leave configurations for the user:
|
|
|
|
|
|
```md
|
|
|
--*- Default netif name for P-NET --->
|
|
|
- -> (e00) default ethernet interface name for p-net app, default as 'e00'
|
|
|
--*- Enable P-NET sample board config --->
|
|
|
- -> (0x0209) p-net user led pin
|
|
|
+-*- Default netif name for P-NET --->
|
|
|
+ -> (e00) default ethernet interface name for p-net app, default as 'e00
|
|
|
+-*- Enable P-NET sample board config --->
|
|
|
+ -> (0x0209) p-ent user led pin
|
|
|
-> (0x0005) p-net user key pin
|
|
|
--*- Default root filesystem path for P-NET --->
|
|
|
+-*- Default root filesystem path for P-NET --->
|
|
|
-> [*] p-net using ramfs filesystem by default, or you can turn this off and choose another way to enable the filesystem
|
|
|
- -> (8192) default memory size for ramfs
|
|
|
--*- P-NET sample slave network ip config --->
|
|
|
- -> (192.168.137.196) set static ip address for Profinet slave
|
|
|
- -> (192.168.137.1) set static gateway address for Profinet slave
|
|
|
- -> (255.255.255.0) set static mask address for Profinet slave
|
|
|
- version (latest) --->
|
|
|
+ -> (8192) default memory size for ramfs
|
|
|
+-*- P-NET sample slave network ip config --->
|
|
|
+ -> (192.168.10.100) set static ip address for profinet slaver
|
|
|
+ -> (192.168.10.1) set static gateway address for profinet slaver
|
|
|
+ -> (255.255.255.0) set static mask address for profinet slaver
|
|
|
+ version (latest) --->
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
* **Default netif name for p-net**: P-net network interface device name, default as e00.
|
|
|
@@ -52,11 +52,11 @@ After completing the configuration, compile and download the program to the deve
|
|
|
|
|
|
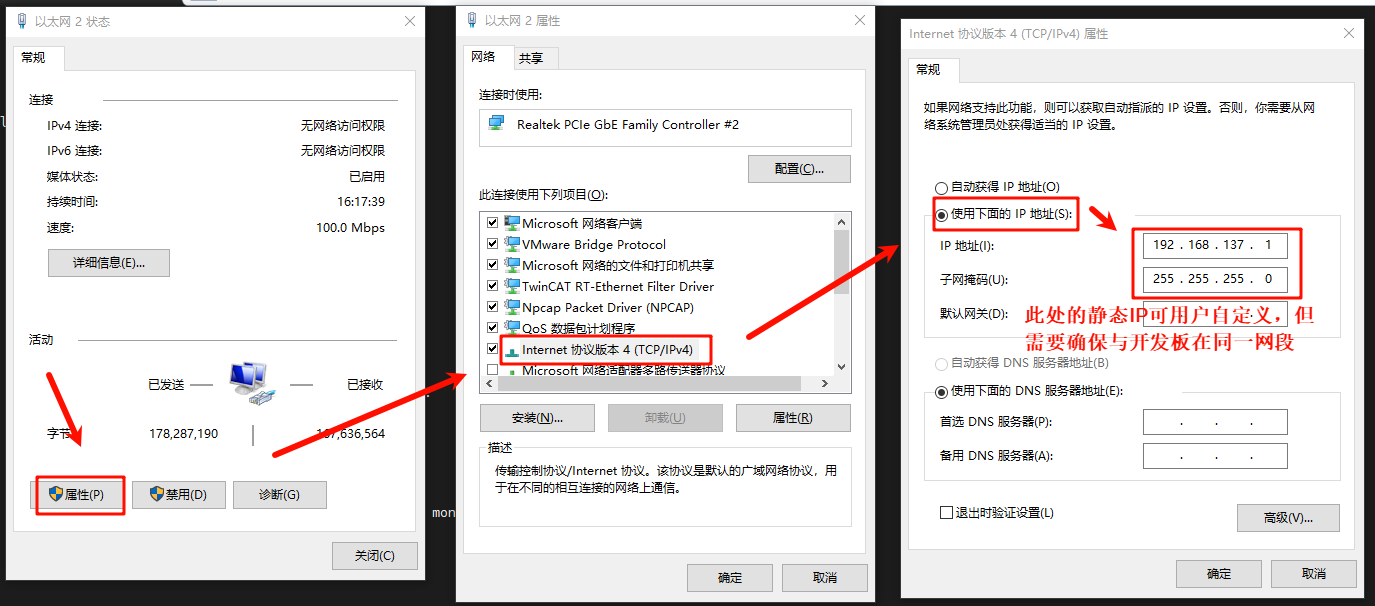
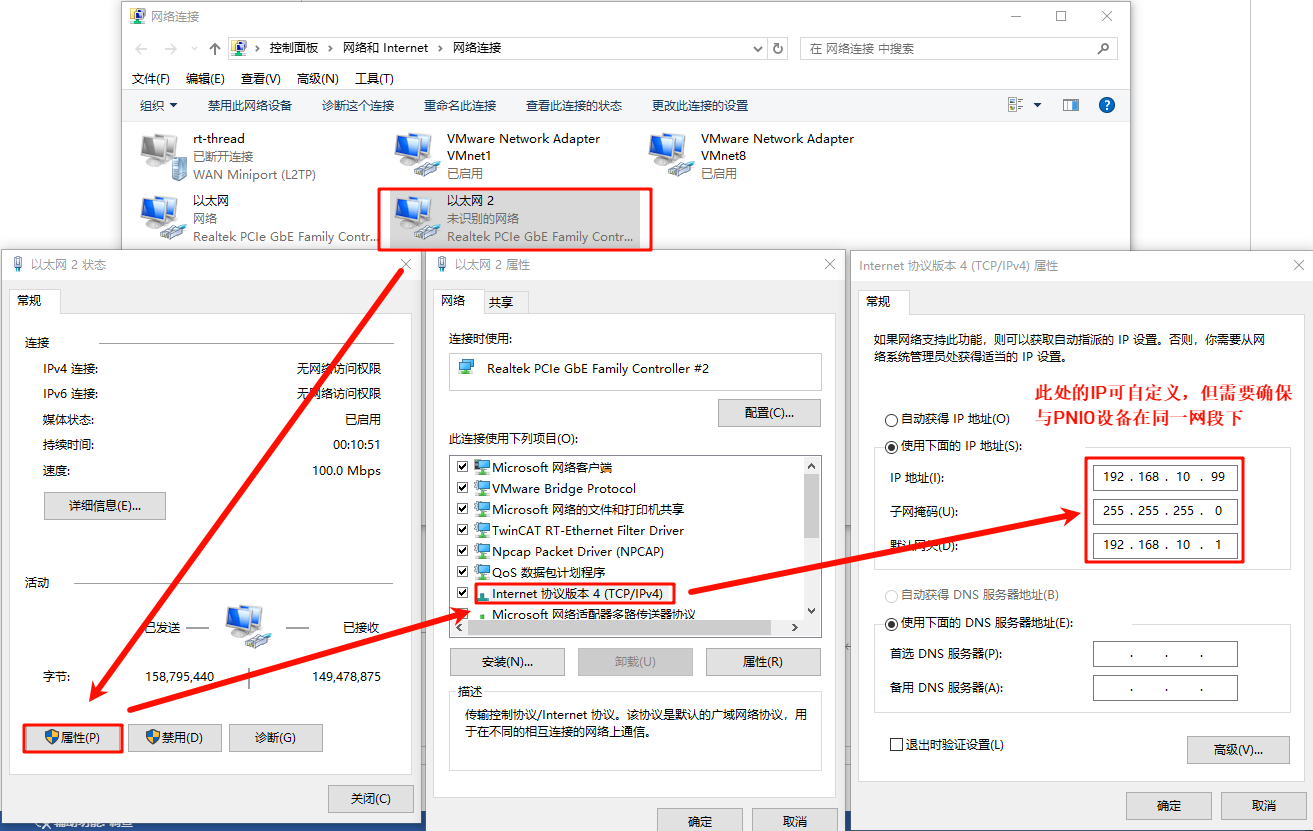
Connect the development board to the PC using an Ethernet cable, and configure a static IP on the PC side:
|
|
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
|
|
|
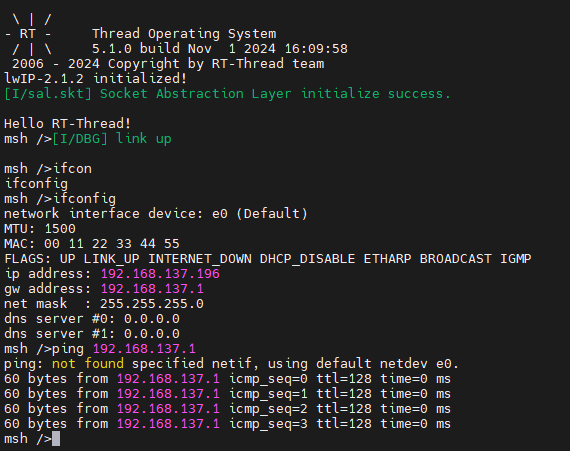
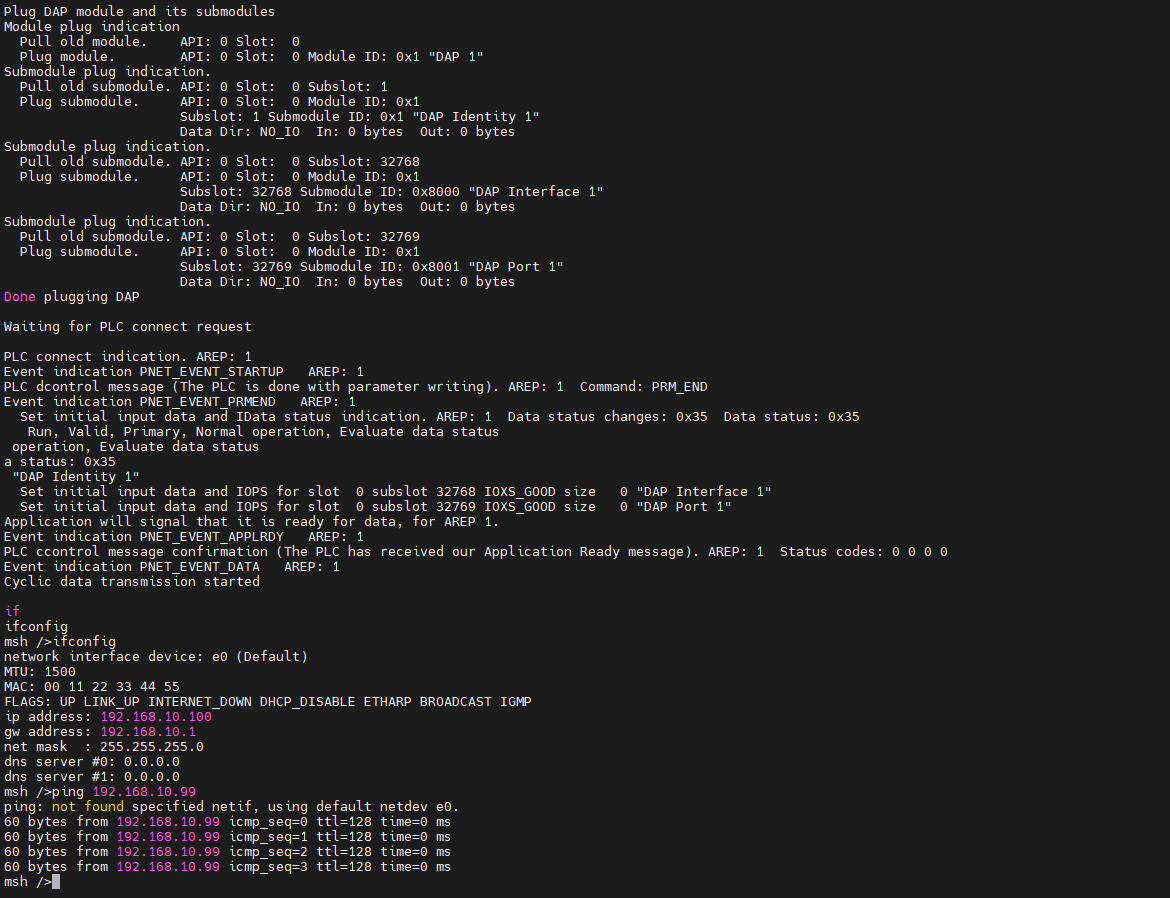
Check the IP information on the development board and test the connectivity:
|
|
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
|
|
|
## 4. SoftPLC Master Startup
|
|
|
|
|
|
@@ -76,7 +76,7 @@ First, open **CODESYS V3.5 SP20 Patch 3**, select -> New Project -> Projects ->
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
-After this popup window appears, click OK to keep the default configuration:
|
|
|
+After the following popup, keep the default Settings (CODESYS Control Win V3 (CODESYS)/x64 (CODESYS)) and click OK:
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
@@ -149,18 +149,18 @@ After the installation is successful, you will see the P-net slave description f
|
|
|
|
|
|
### 4.6 Network Configuration
|
|
|
|
|
|
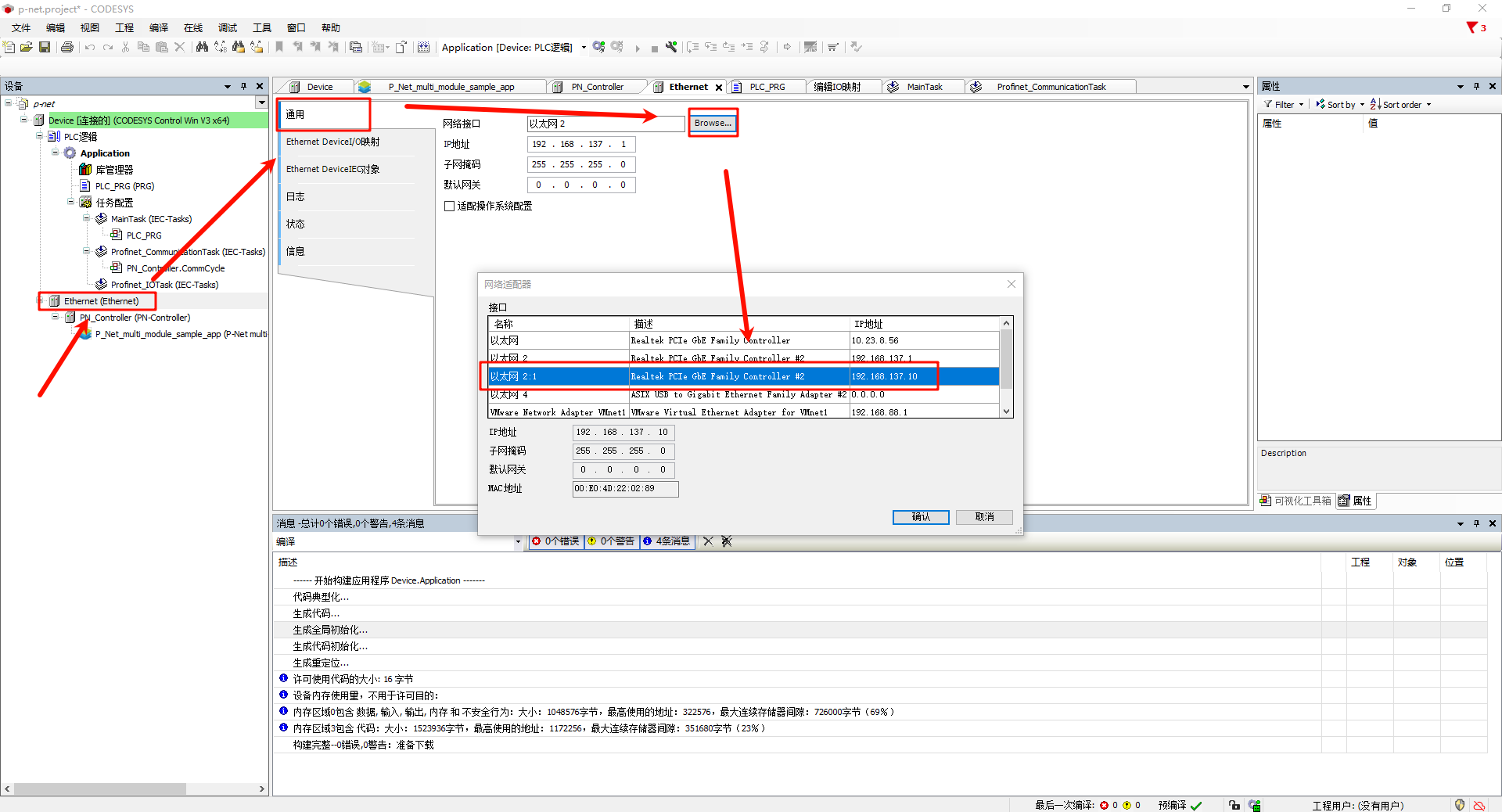
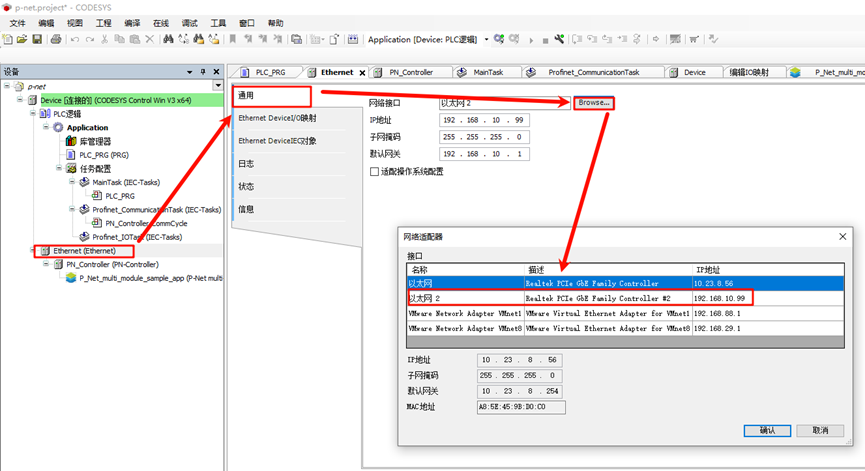
-* **Ethernet configuration**: Double-click **Ethernet (Ethernet)** on the left navigation panel -> General, and change the network interface to the Ethernet port connected to the development board (since I enabled PRONETA, two master IPs are assigned within the same subnet, so make sure to choose the correct one):
|
|
|
+* **Ethernet configuration**: Double-click **Ethernet (Ethernet)** on the left navigation panel -> General, and change the network interface to the Ethernet port connected to the development board;
|
|
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
|
|
|
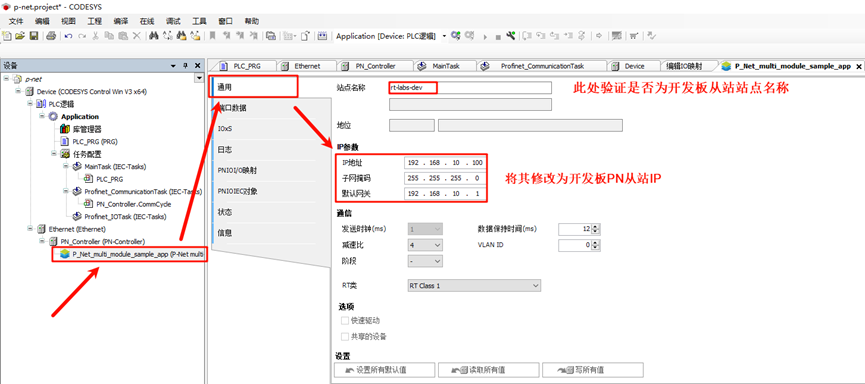
* **PN_Controller configuration**: Double-click **PN_Controller (PN-Controller)** on
|
|
|
|
|
|
the left navigation panel -> General, and modify the default slave IP parameters according to the prompts.
|
|
|
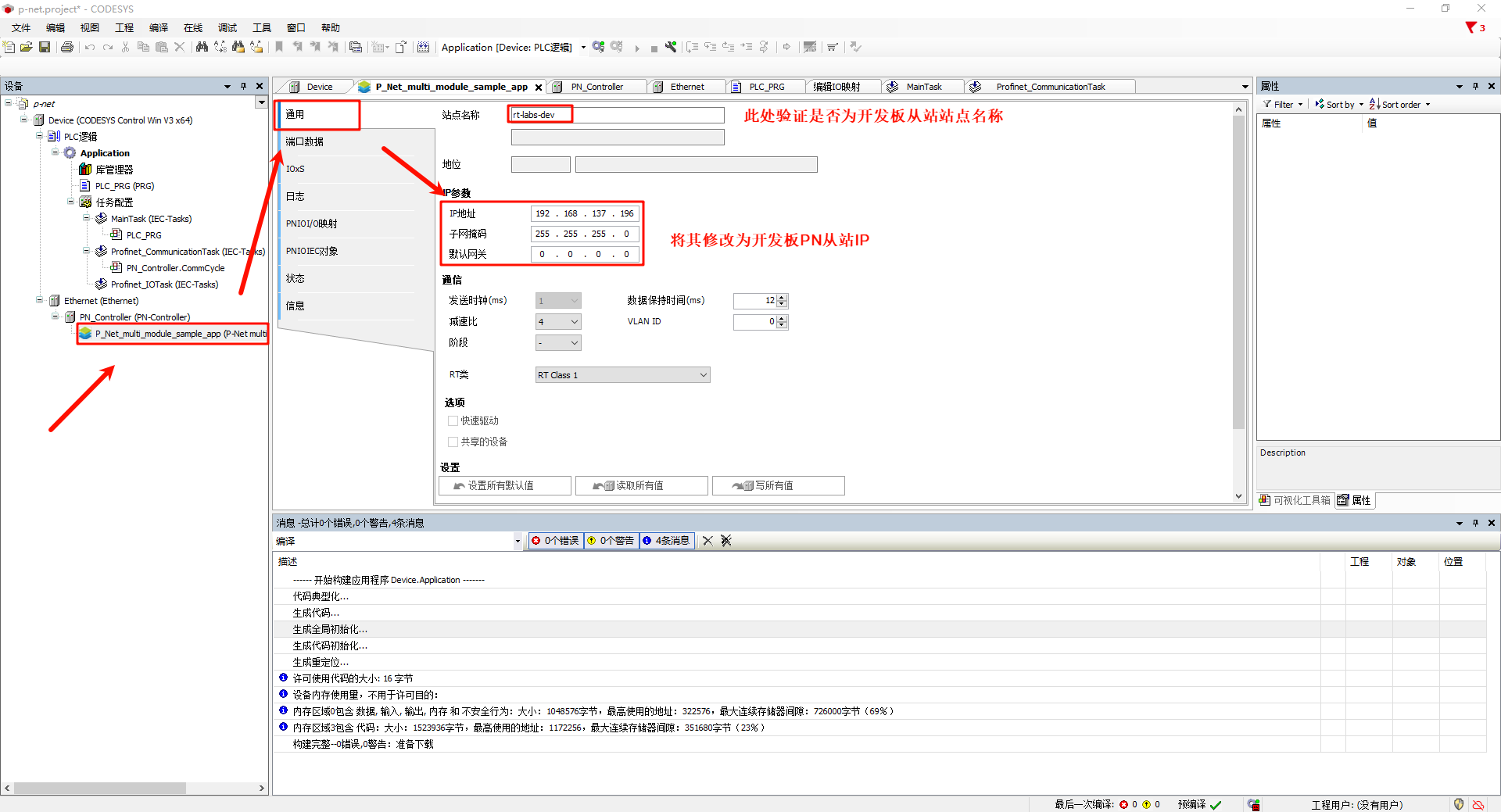
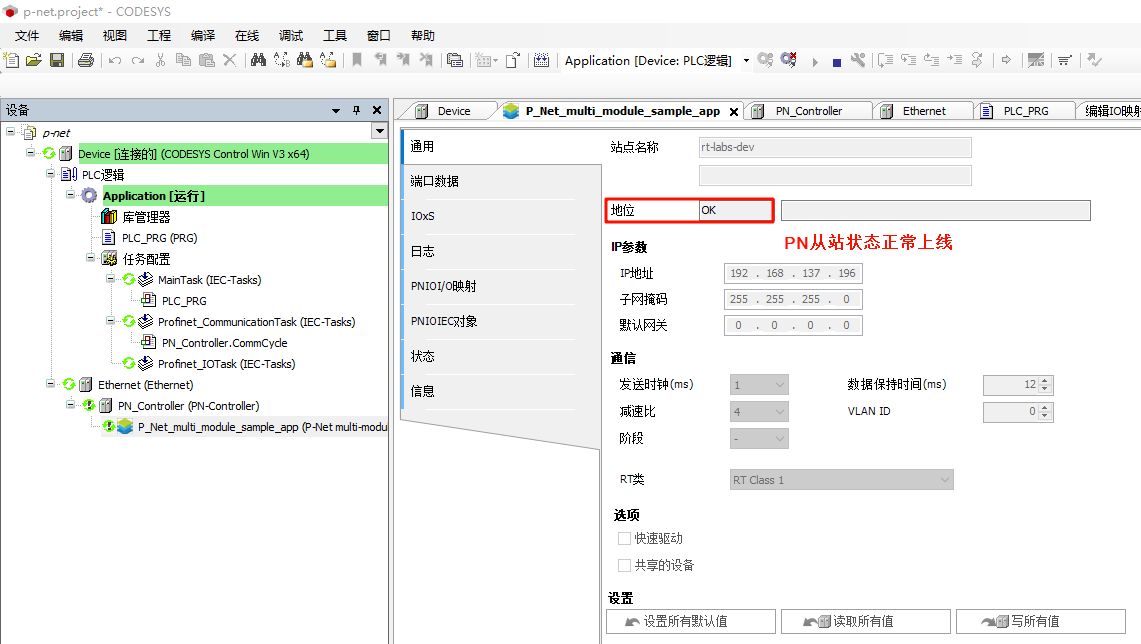
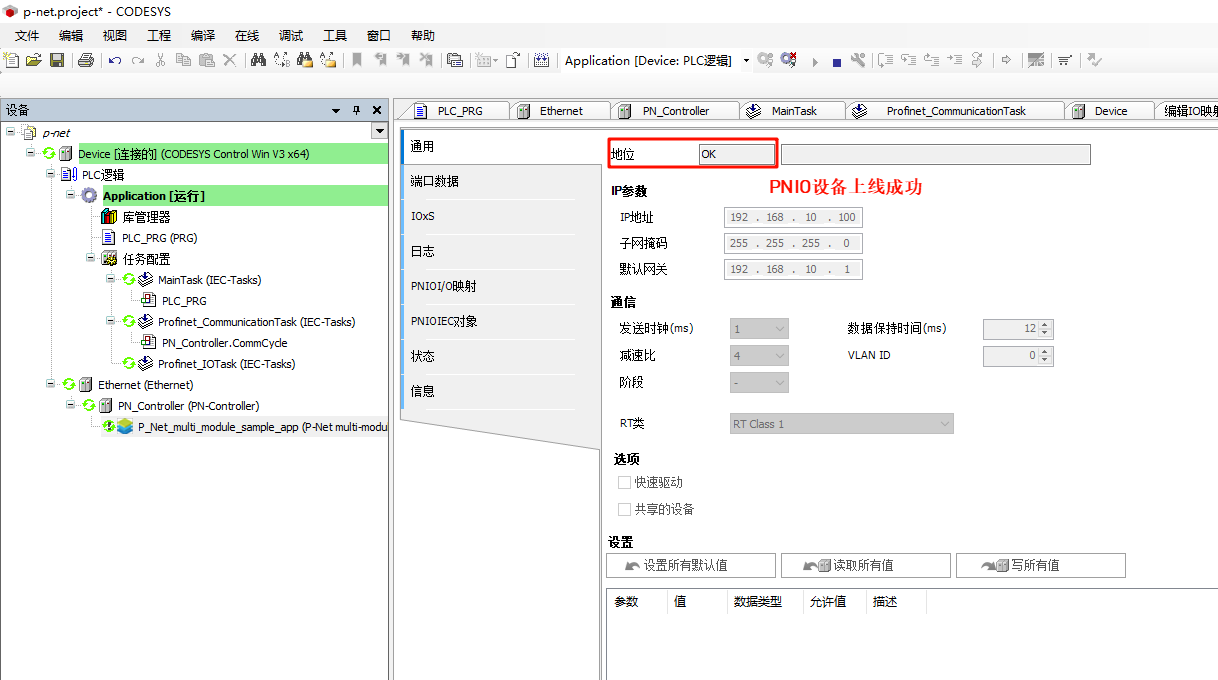
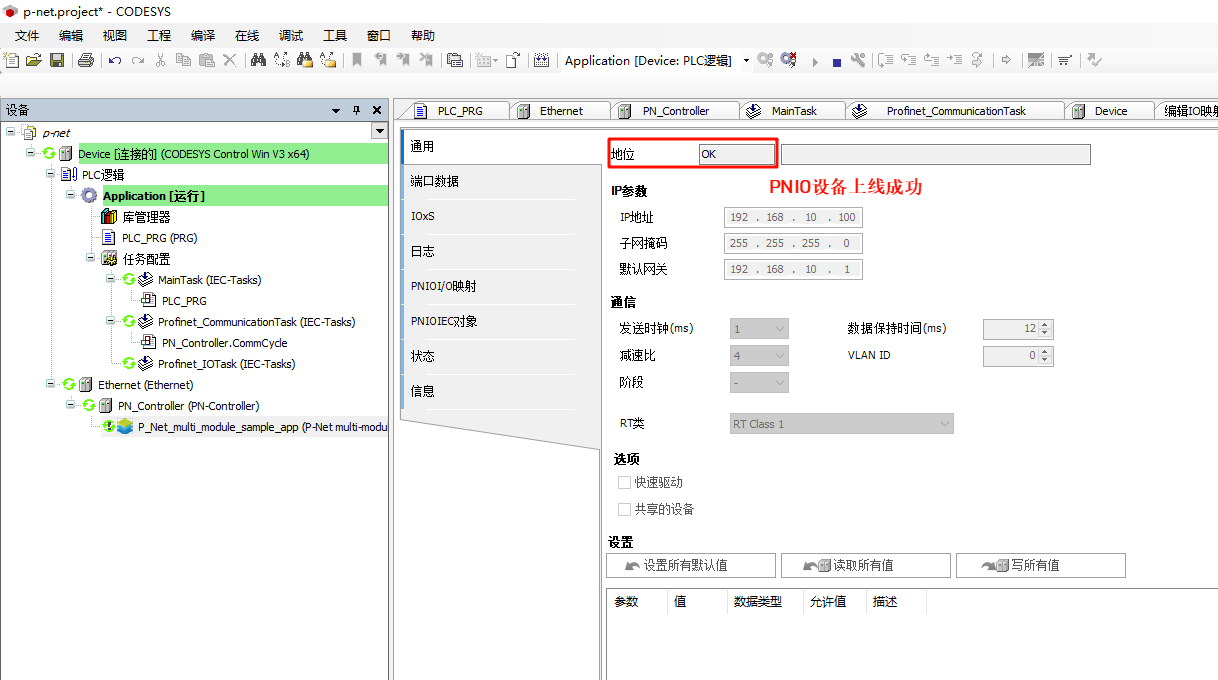
* **P-Net Slave network configuration**: Double-click **P-Net-multiple-module sample app** on the left navigation panel -> General, and change the IP parameters to the development board's IP:
|
|
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
|
|
|
### 4.7 Compile, Debug, and Start the Project
|
|
|
|
|
|
@@ -174,11 +174,11 @@ You should now see that the PN master has successfully come online:
|
|
|
|
|
|
## 5. Profinet Slave Application Startup
|
|
|
|
|
|
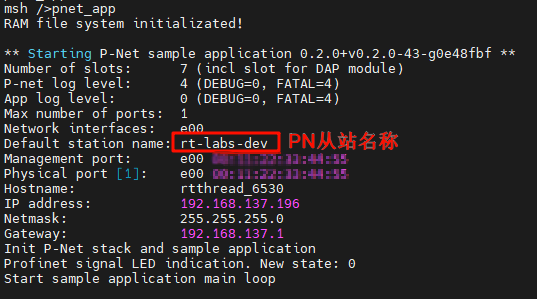
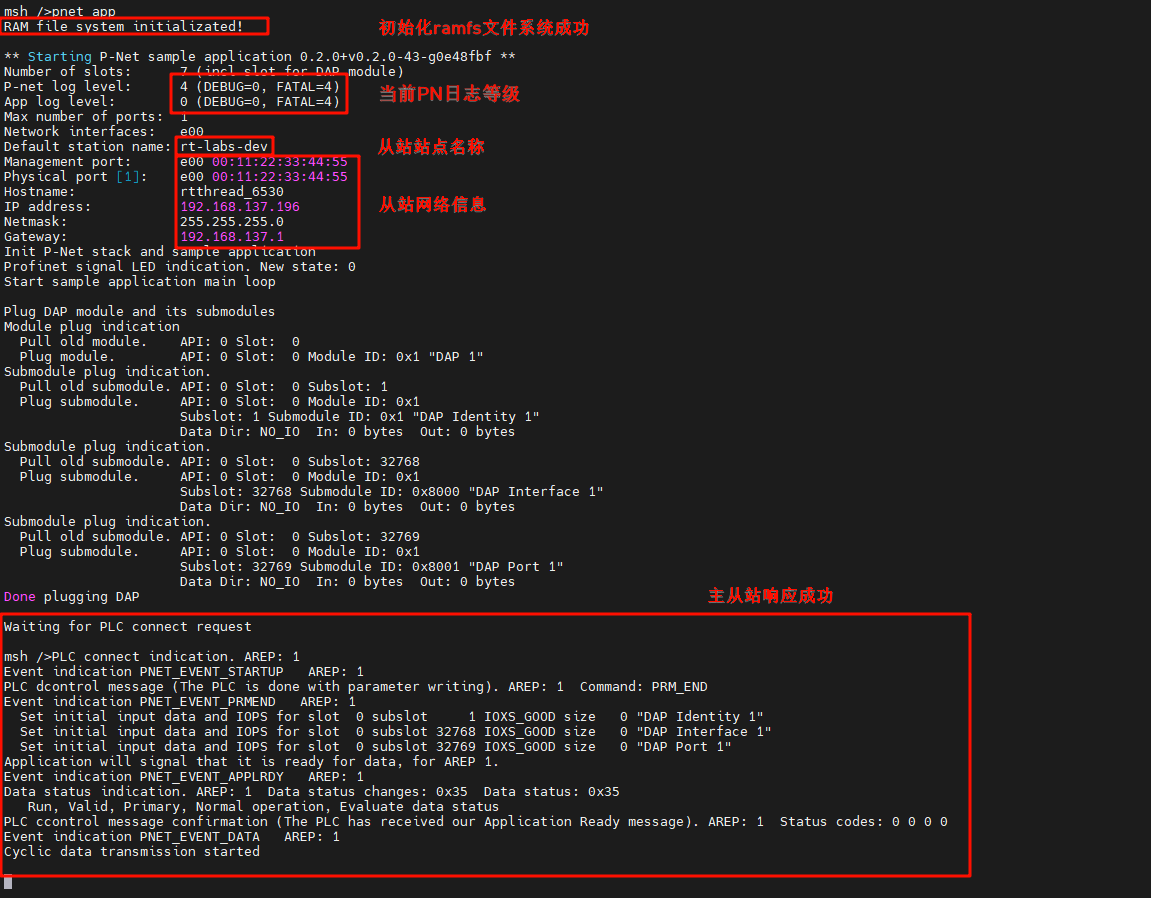
-Start the PN slave on the development board by executing the command: `pnet_app`:
|
|
|
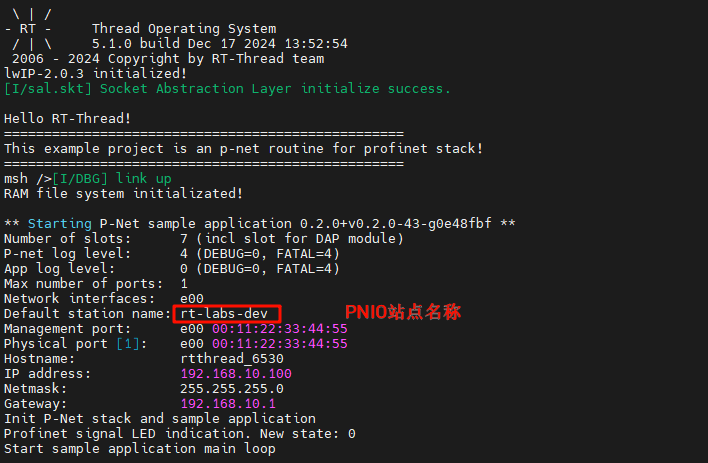
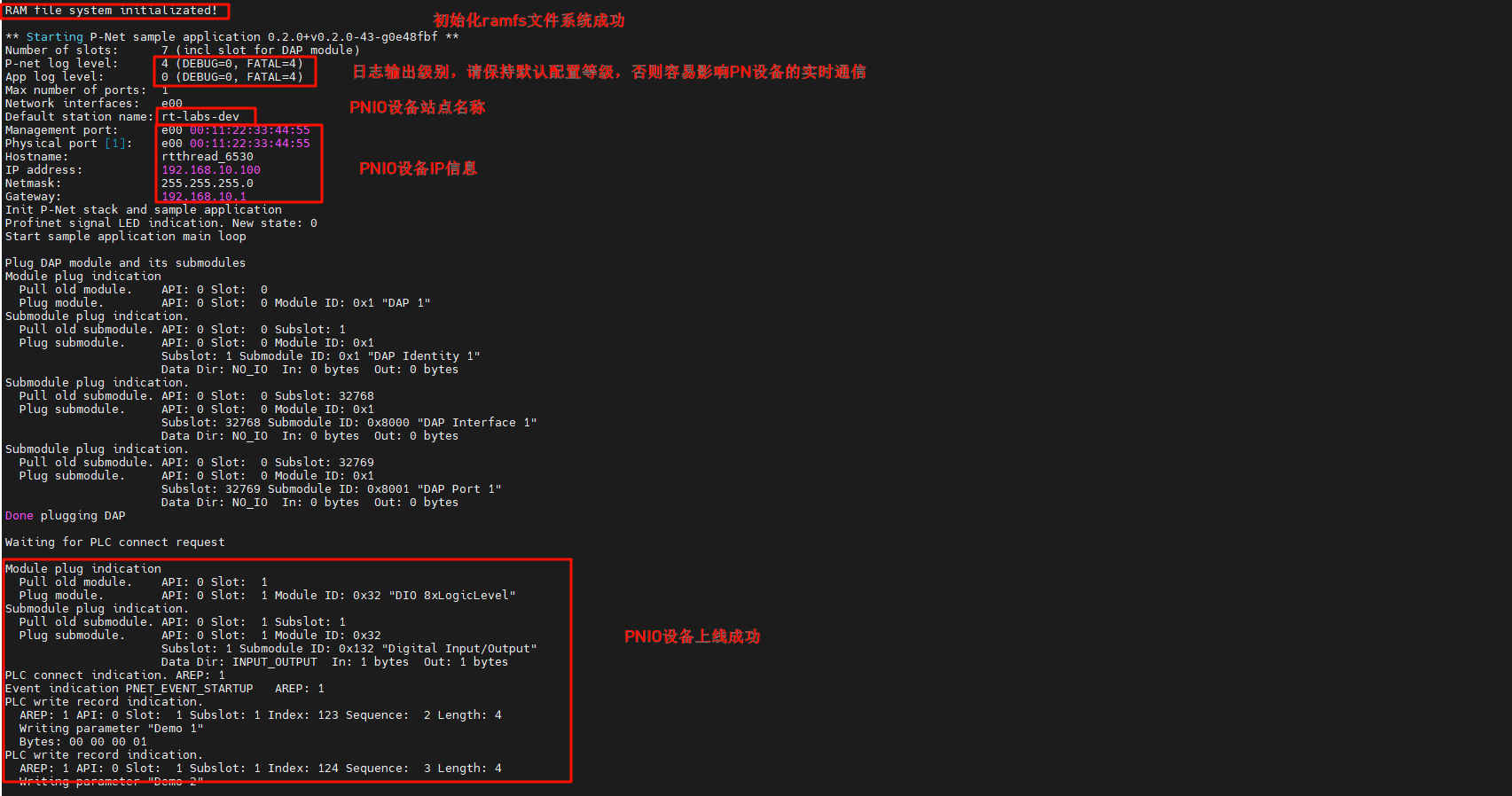
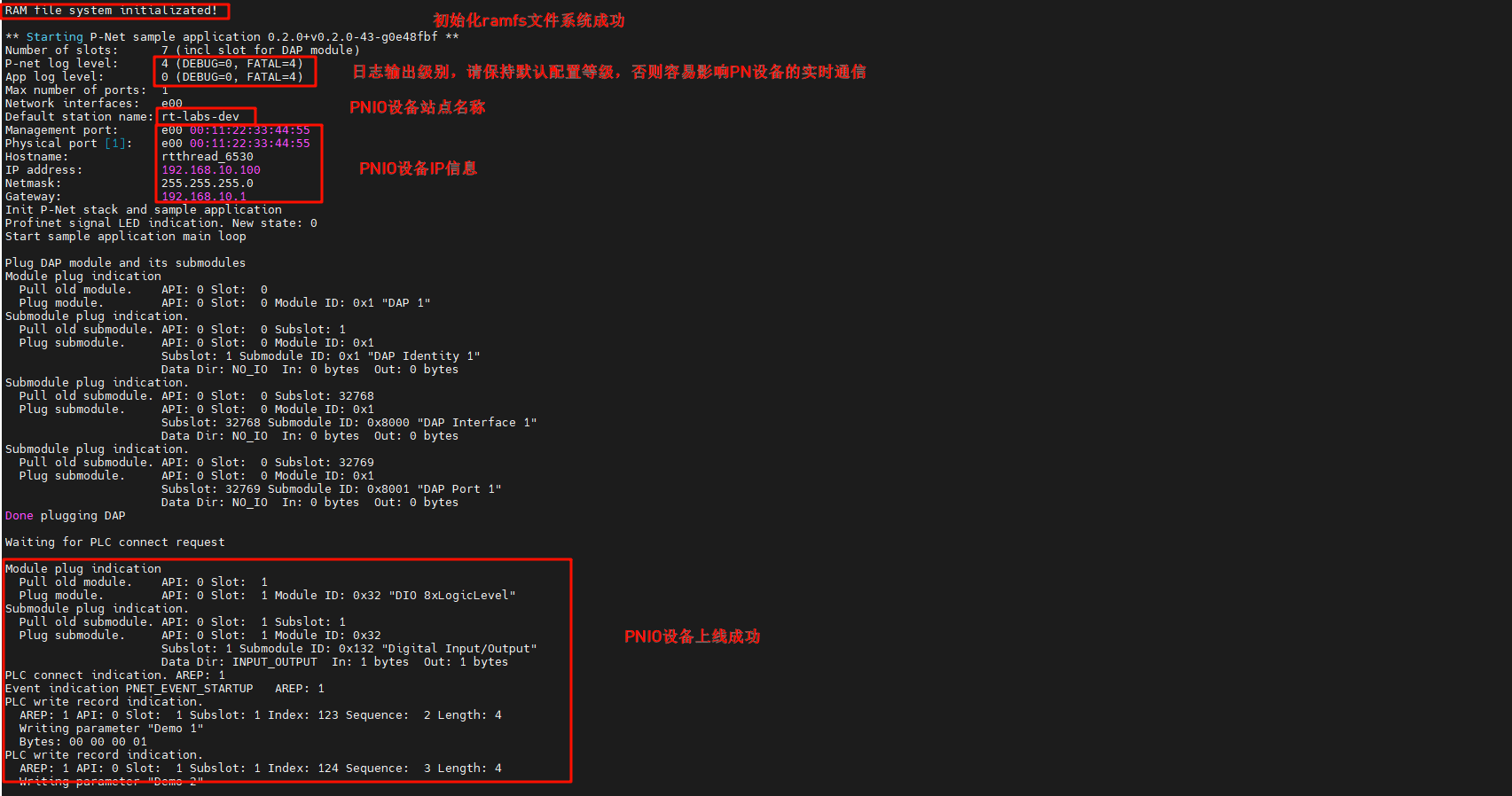
+After the development board is powered on, once the NIC link up is detected, the secondary PN station is automatically started:
|
|
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
|
|
|
## 6. PN Protocol Stack Demo
|
|
|
|
|
|
@@ -206,11 +206,74 @@ PNIO will update the slave configuration information:
|
|
|
|
|
|
Click **I&M** again to see that the I&M modification has been successfully applied!
|
|
|
|
|
|
-### 6.3 PN Network Topology
|
|
|
+### 6.3 PLC Programming and PNIO Control
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
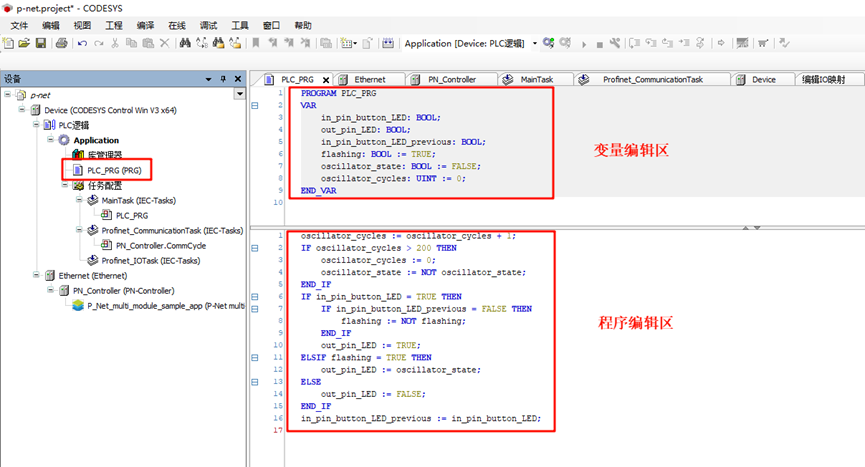
+First, click on the left panel to navigate to Device -> PLC Logic -> Application -> PLC_PRG(PRG), and use ST (Structured Text) language to program, defining variables and writing program code:
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+* **Variable Definitions**: These variables define the input state of the button (`in_pin_button_LED`), the output state of the LED (`out_pin_LED`), and the state variable controlling whether the LED should blink (`flashing`). The oscillator state (`oscillator_state`) and oscillator cycle counter (`oscillator_cycles`) are used to create the blinking effect.
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+```st
|
|
|
+PROGRAM PLC_PRG
|
|
|
+VAR
|
|
|
+ in_pin_button_LED: BOOL;
|
|
|
+ out_pin_LED: BOOL;
|
|
|
+ in_pin_button_LED_previous: BOOL;
|
|
|
+ flashing: BOOL := TRUE;
|
|
|
+ oscillator_state: BOOL := FALSE;
|
|
|
+ oscillator_cycles: UINT := 0;
|
|
|
+END_VAR
|
|
|
+```
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+* **Program Definition**:
|
|
|
+ 1. First, in each cycle, the `oscillator_cycles` is incremented by 1. When the counter exceeds 200, it resets the counter and toggles the `oscillator_state` (TRUE or FALSE) to create periodic changes.
|
|
|
+ 2. If the button is pressed (`in_pin_button_LED` is TRUE) and the previous cycle's button state was FALSE, the `flashing` state is toggled. This means every time the button is pressed, the LED blinking state will toggle.
|
|
|
+ 3. If `flashing` is TRUE, the LED will blink according to the `oscillator_state`. If `flashing` is FALSE, the LED will be turned off.
|
|
|
+ 4. At the end of each cycle, the current button state is saved in `in_pin_button_LED_previous` to detect the next button press event.
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+```st
|
|
|
+oscillator_cycles := oscillator_cycles + 1;
|
|
|
+IF oscillator_cycles > 200 THEN
|
|
|
+ oscillator_cycles := 0;
|
|
|
+ oscillator_state := NOT oscillator_state;
|
|
|
+END_IF
|
|
|
+IF in_pin_button_LED = TRUE THEN
|
|
|
+ IF in_pin_button_LED_previous = FALSE THEN
|
|
|
+ flashing := NOT flashing;
|
|
|
+ END_IF
|
|
|
+ out_pin_LED := TRUE;
|
|
|
+ELSIF flashing = TRUE THEN
|
|
|
+ out_pin_LED := oscillator_state;
|
|
|
+ELSE
|
|
|
+ out_pin_LED := FALSE;
|
|
|
+END_IF
|
|
|
+in_pin_button_LED_previous := in_pin_button_LED;
|
|
|
+```
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+The configuration in the project is shown in the image below:
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
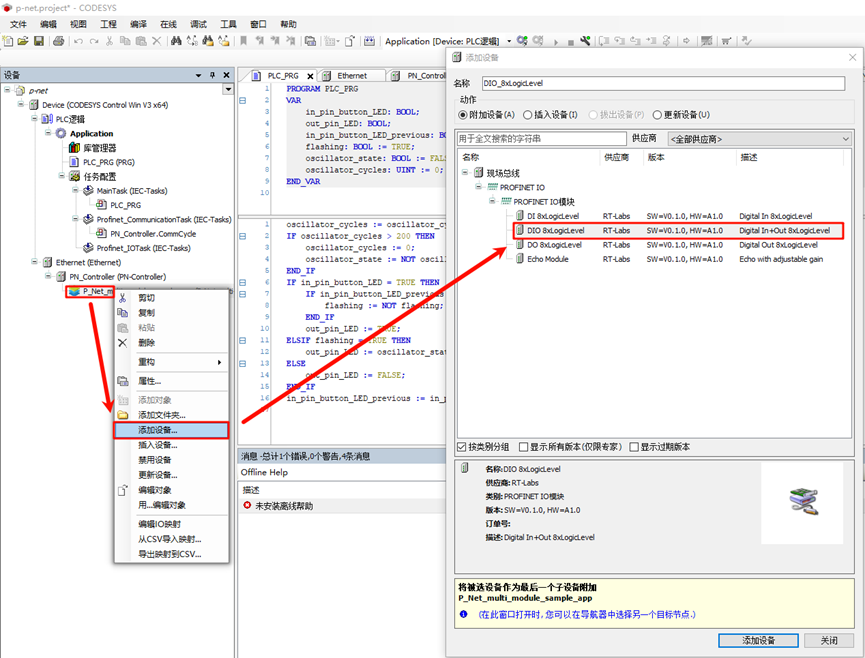
+Next, we need to add a built-in I/O module. Right-click on `P_Net_multi_module_sample_app` and add an I/O module (DIO 8xLogicLevel), as shown in the following image:
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
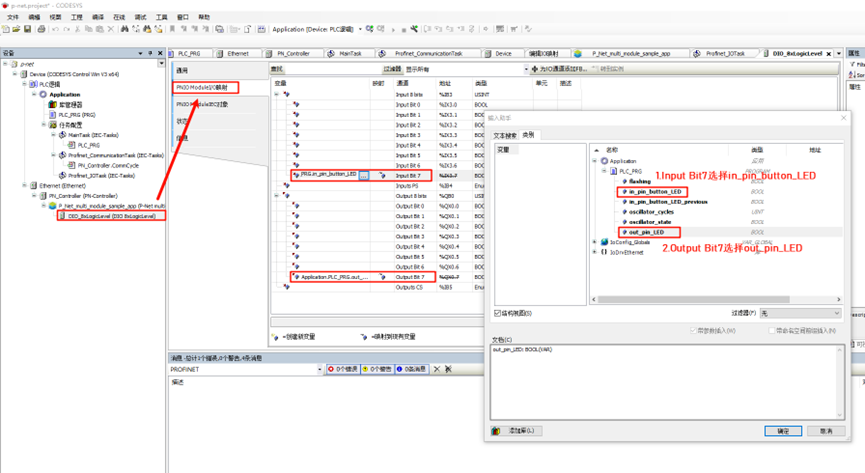
+Next, double-click the `DIO_8xLogicLevel` node, select `PNIO Module I/O Mapping`, and edit `Input Bit 7` and `Output Bit 7`, binding them to the PLC variables:
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
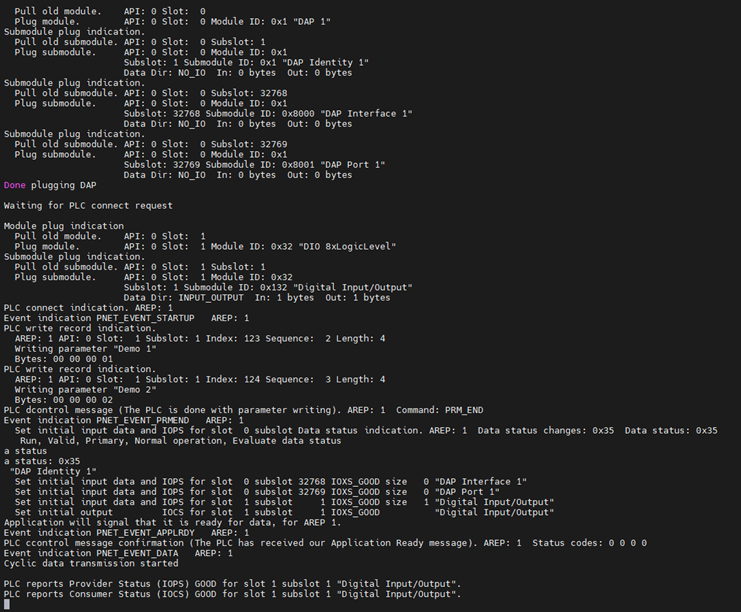
+Then, click on the "Compile -> Generate Code" in the top navigation bar, followed by "Online -> Login", and run the program to observe the phenomenon:
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
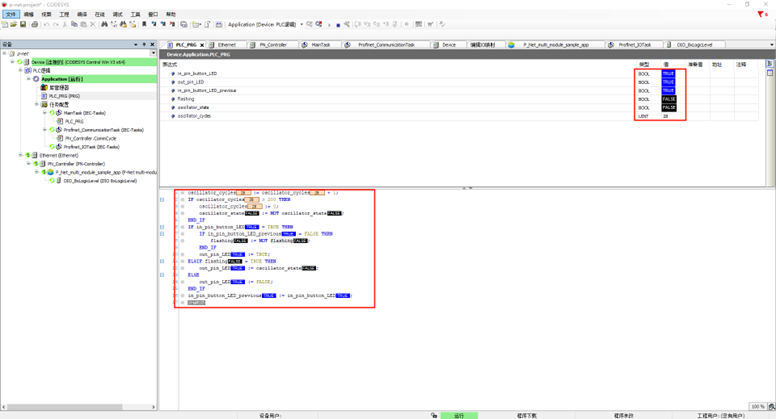
+Next, return to CODESYS and double-click on Device -> PLC Logic -> Application -> PLC_PRG(PRG). At this point, you can dynamically observe the program's running status. For example, by holding down the KEY0 button on the EtherKit development board, you can see that the values of `in_pin_button_LED` and `in_pin_button_LED_previous` are both FALSE. When you release KEY0, the value of `flashing` will toggle once.
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+### 6.4 PN Network Topology
|
|
|
|
|
|
> PRONETA Overview: PRONETA Basic is a simple tool for quickly analyzing and configuring PROFINET networks. It also supports basic testing of ET 200 distributed IO systems and other components.
|
|
|
|
|
|
-#### 6.3.1 Install GSDML Files
|
|
|
+#### 6.4.1 Install GSDML Files
|
|
|
|
|
|
Open the PRONETA software and add the GSDML file:
|
|
|
|
|
|
@@ -220,13 +283,13 @@ After installation is successful, you can see the status information:
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
-#### 6.3.2 Select Network Adapter
|
|
|
+#### 6.4.2 Select Network Adapter
|
|
|
|
|
|
Click **Settings -> Network Adapter** and choose the PN corresponding Ethernet port:
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
-#### 6.3.3 View Online Network Status
|
|
|
+#### 6.4.3 View Online Network Status
|
|
|
|
|
|
Select **Network Analysis -> Online** from the top left navigation panel, click **Refresh**, and after a moment, you should see the PN network status. The specific PNIO information can be viewed on the right sidebar. Since we modified the PNIO information in CODESYS, you can also see the updated information here.
|
|
|
|